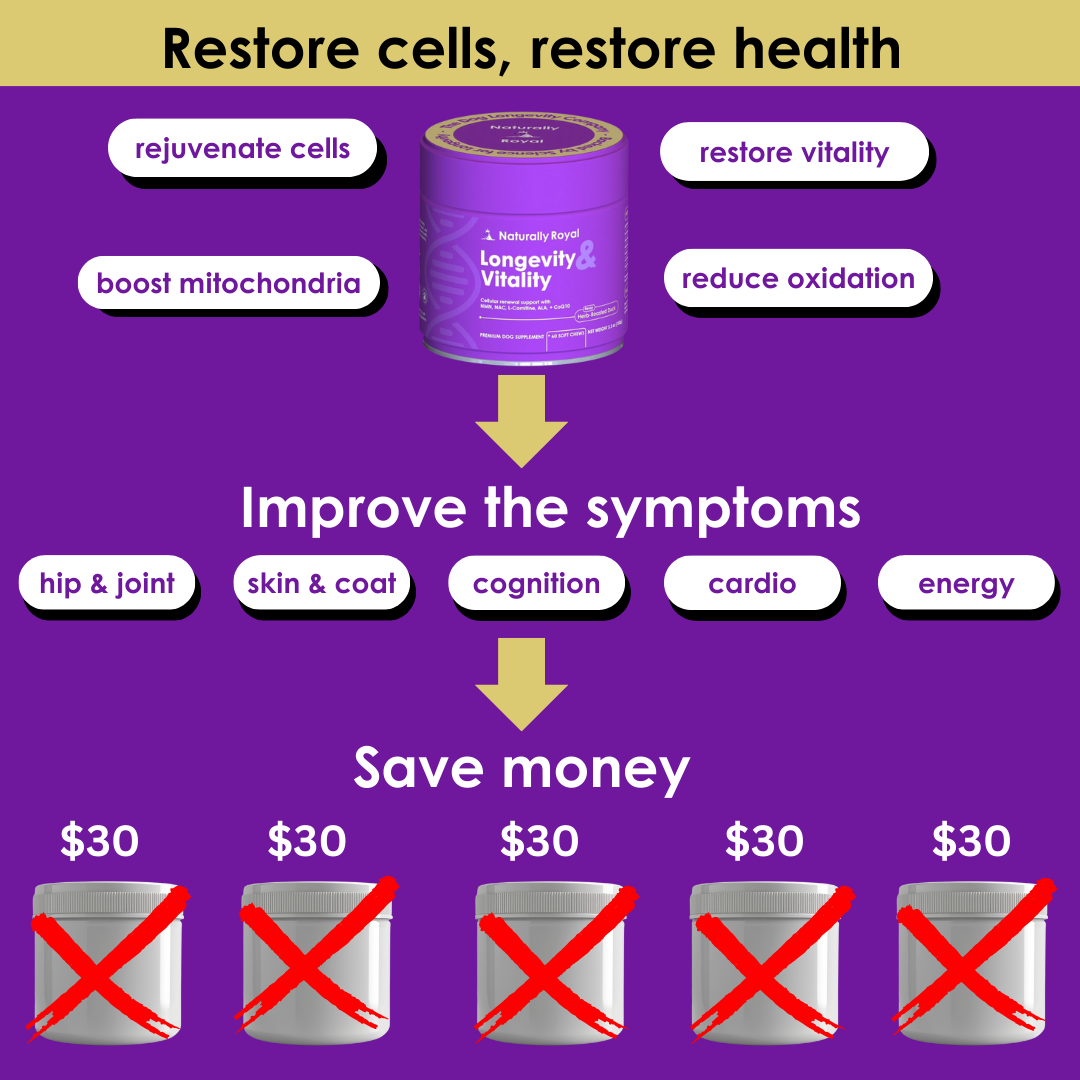
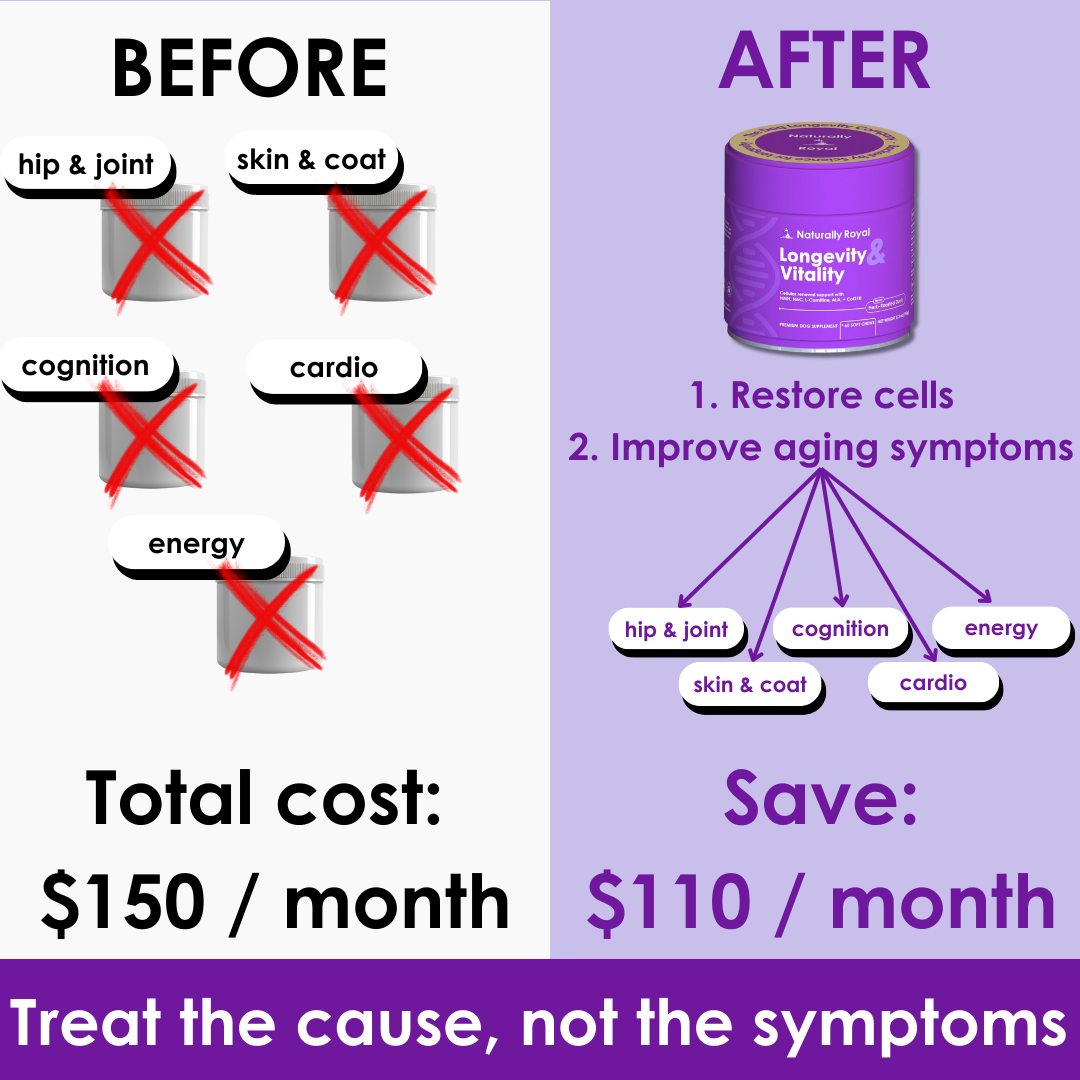
What Your Dog’s Blood Work Says About Their Longevity
Understanding your dog’s health is key to ensuring they live a long, happy life, and blood tests like blood chemistry panels and complete blood counts (CBCs) are essential tools for unlocking important insights. These tests provide a window into your dog’s internal systems, allowing veterinarians to assess organ function, detect hidden diseases, and predict longevity.
Let's do a dive deep into what these blood tests tell you about your dog’s health and how these results can give you an indication of your dog’s potential longevity:
What Is a Blood Chemistry Panel?
A blood chemistry panel measures the levels of various chemicals in your dog’s blood, providing an overview of organ function and metabolic health. This test evaluates multiple substances, including enzymes, electrolytes, lipids, proteins, and waste products. The most important components of a blood chemistry panel include:
-
Liver Function
- Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT): Elevated levels indicate liver cell damage or dysfunction. Persistent increases could signal liver disease or chronic inflammation.
- Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): High levels can be associated with liver disease, bone disorders, or Cushing's disease. Chronic elevation often points to an underlying condition affecting liver or bone health.
Longevity Implications: Liver function is crucial for detoxification and nutrient processing. Chronic liver dysfunction, if untreated, can significantly shorten your dog’s lifespan. Early detection allows for interventions that can improve or stabilize liver health.
-
Kidney Function
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) and Creatinine: These are waste products filtered by the kidneys. Elevated levels indicate reduced kidney function, signaling possible kidney disease or failure.
- Phosphorus: Increased phosphorus levels may accompany kidney dysfunction, particularly in advanced stages of kidney disease.
Longevity Implications: Kidney disease is common in older dogs and can progress silently over time. Monitoring kidney markers allows for early intervention, which can slow down the progression of kidney disease, extending your dog's lifespan.
-
Pancreas Function
- Amylase and Lipase: These enzymes are involved in digestion. Elevated levels may indicate pancreatitis or pancreatic insufficiency, which can affect nutrient absorption and overall health.
Longevity Implications: Chronic pancreatitis can lead to malnutrition and recurring health issues. Early detection and management can help maintain pancreatic health, supporting your dog’s longevity.
-
Blood Sugar Levels
- Glucose: High glucose levels may indicate diabetes mellitus, while low glucose levels (hypoglycemia) can suggest liver disease, Addison’s disease, or other metabolic disorders.
Longevity Implications: Proper blood sugar regulation is essential for energy balance and preventing metabolic diseases like diabetes, which, if unmanaged, can drastically shorten a dog’s life.
-
Electrolytes
- Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Chloride (Cl): These minerals are essential for nerve and muscle function, fluid balance, and cellular health. Imbalances may indicate dehydration, Addison’s disease, or kidney issues.
Longevity Implications: Electrolyte imbalances can lead to life-threatening conditions, especially in dogs with kidney disease or heart issues. Correcting these imbalances helps maintain overall health and longevity.
-
Proteins
- Albumin and Globulin: These proteins are essential for maintaining fluid balance and immune function. Low levels may indicate liver disease, kidney disease, or gastrointestinal issues.
Longevity Implications: Low protein levels can signify chronic illness. Addressing these issues early helps support long-term health and resilience against diseases that can reduce lifespan.
What Is a CBC (Complete Blood Count)?
A CBC analyzes your dog’s red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, providing essential information about their immune function, oxygen-carrying capacity, and blood clotting abilities. Key components of the CBC include:
-
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
- Hemoglobin (HGB) and Hematocrit (HCT): These measure the oxygen-carrying capacity of your dog’s blood. Low levels (anemia) can indicate blood loss, chronic disease, or bone marrow disorders.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): This measures the size of red blood cells. Large RBCs can indicate regeneration following blood loss, while small RBCs may suggest iron deficiency.
Longevity Implications: Chronic anemia or issues with red blood cell production can weaken your dog and limit their energy levels. Ensuring proper oxygen transport through healthy RBCs supports overall vitality and can extend lifespan.
-
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
- Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophils, and Basophils: These cells are critical for immune response. High levels may indicate infections, inflammation, or stress, while low levels may suggest immune suppression or bone marrow issues.
Longevity Implications: A balanced and effective immune system helps your dog fight off infections and diseases. Chronic immune dysfunction or unaddressed infections can weaken the body over time, leading to a shortened life expectancy.
-
Platelets (PLT)
- Platelet Count: Platelets are essential for blood clotting. Low platelet counts can indicate conditions like immune-mediated thrombocytopenia or bone marrow disorders, while high counts may be seen in inflammatory conditions.
Longevity Implications: Adequate platelet levels are crucial for preventing internal bleeding and promoting healing. Chronic low platelet counts can increase the risk of hemorrhage and may signal underlying health problems that affect longevity.
How These Results Relate to Longevity
Blood chemistry panels and CBC results provide critical insights into your dog’s overall health. Here’s how they contribute to longevity:
-
Early Detection of Diseases: Blood tests can detect diseases like kidney failure, liver disease, diabetes, and cancer long before symptoms appear. Catching these conditions early allows for timely interventions, which can prolong your dog’s life.
-
Monitoring Age-Related Decline: As dogs age, their organs may naturally begin to lose function. Regular blood tests allow you to monitor these changes and adjust your dog’s diet, supplements, or medications to support their aging process and maintain their quality of life.
-
Customizing Care: Knowing your dog’s baseline blood chemistry and CBC levels allows your veterinarian to tailor your dog’s care to their specific needs, ensuring that they receive targeted treatment that maximizes their health and longevity.
-
Preventing Crises: Abnormal blood test results can warn of potential health crises, like kidney failure or heart disease, before they become emergencies. Preventing or managing these crises is key to extending your dog’s life.
-
Nutritional and Supplementary Adjustments: Blood tests reveal how well your dog’s body processes nutrients, which can help guide decisions on diet, supplements, or medications. This ensures your dog is receiving the nutrients they need for optimal health and longevity.
Conclusion
Understanding your dog’s blood chemistry and CBC results can provide profound insights into their health and longevity. Regular blood tests, especially as your dog ages, are essential for detecting early signs of disease, monitoring organ function, and guiding appropriate medical interventions. By staying informed and proactive with your dog’s health, you can help them live a longer, healthier life filled with vitality.