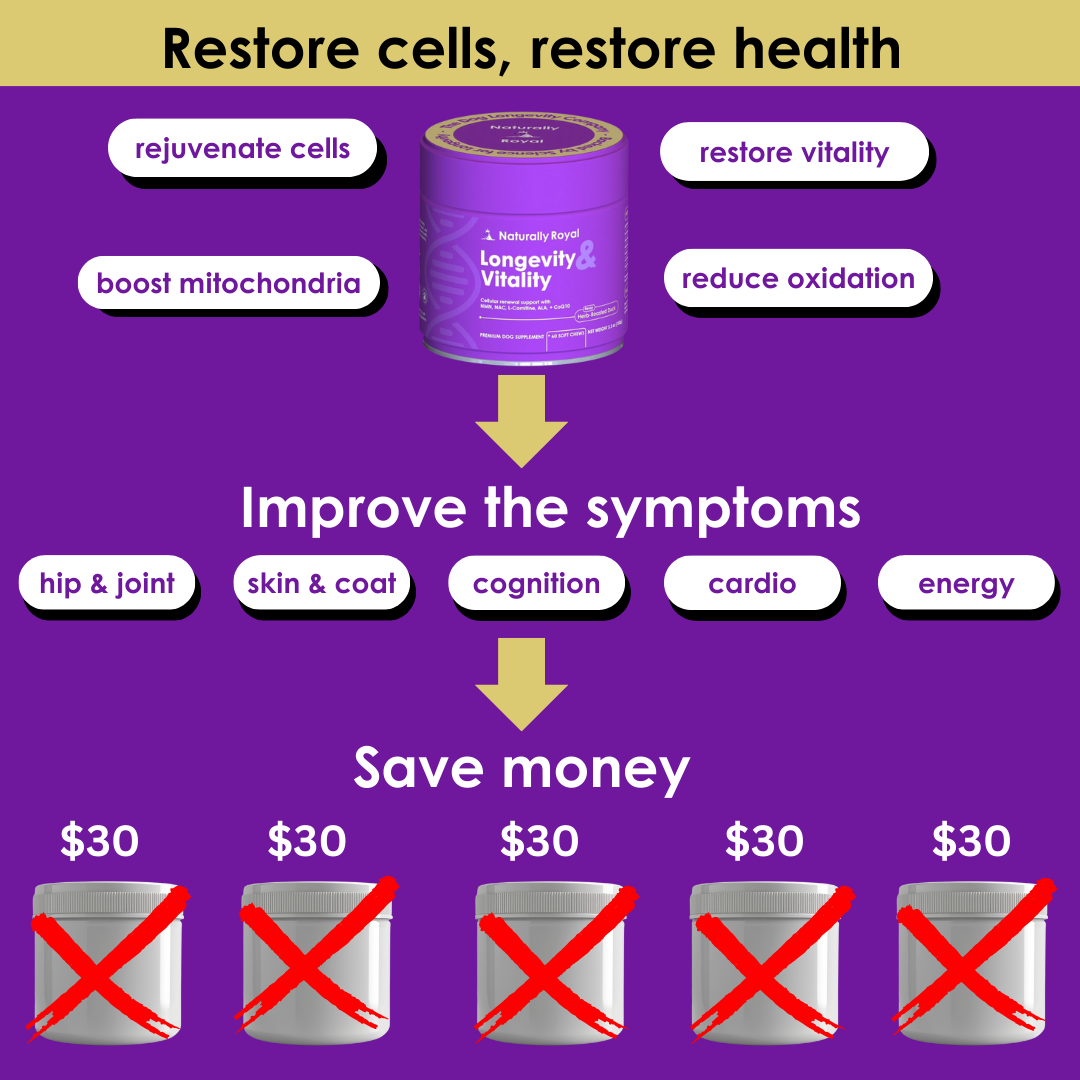
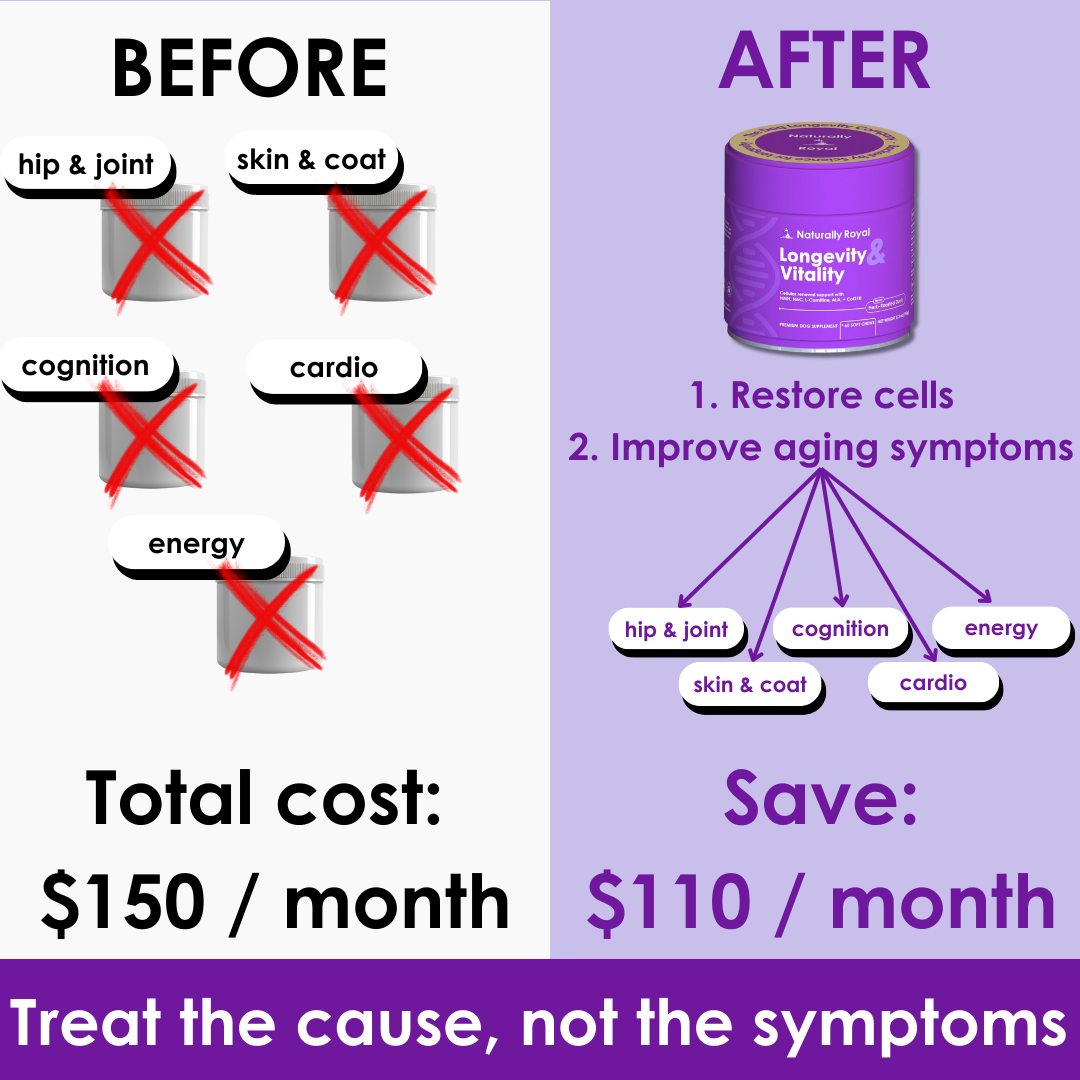
New Study Reveals Longevity Impact of Socialization
A recent study by Arizona State University highlights the profound impact that socialization has on the health and longevity of dogs. The Dog Aging Project, a large-scale initiative involving over 21,000 dogs, found that a robust social support network significantly enhances a dog's well-being, even more so than financial factors, household stability, or the owner's age. Let’s go over the key findings and what that means for longevity:
The Power of Social Connections
-
Strong Social Networks Enhance Health: The study reveals that dogs with strong social connections tend to have better health outcomes. Interaction with both humans and other animals plays a crucial role in improving their overall well-being and extending their lifespan.
-
More Influential Than Financial Stability: Surprisingly, the level of social support a dog receives was found to be five times more impactful on their health than their owner's financial situation. This underscores the importance of quality time and attention over material conditions.
Factors Influencing Dog Health
-
Companionship Matters: Dogs that share their environment with other dogs generally exhibit better health. This companionship provides constant interaction and social engagement, which are critical for mental and physical health.
-
Children's Impact: Interestingly, the study noted a negative correlation between the number of children in a household and a dog's health. This may be due to the diversion of attention and resources away from the dog, underscoring the need for balanced attention.
-
Economic Disparities: Higher-income households tend to have dogs diagnosed with more diseases. This could be due to better access to veterinary care, leading to more frequent and thorough health screenings.
Research Insights and Future Directions
-
Exploring Underlying Mechanisms: The researchers aim to look deeper into how these social factors "get under the skin" to influence a dog's health at a cellular level. Understanding the biological impacts of socialization could lead to more targeted strategies for enhancing dog health and longevity.
-
Longitudinal Studies: Further studies will integrate veterinary records, molecular data, and physical tests to paint a more comprehensive picture of how environmental factors contribute to health and aging.
Implications for Longevity
This study not only illuminates the critical role of social factors in canine health but also mirrors similar dynamics in human health. Ensuring that our dogs have a rich social life, balanced attention, and proper medical care can significantly enhance their quality of life and longevity.